Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Overview, Prevention, and Treatment
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints, leading to inflammation, pain, and potential joint damage. This article provides a detailed overview of rheumatoid arthritis, including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and recommendations for products that can help alleviate pain.
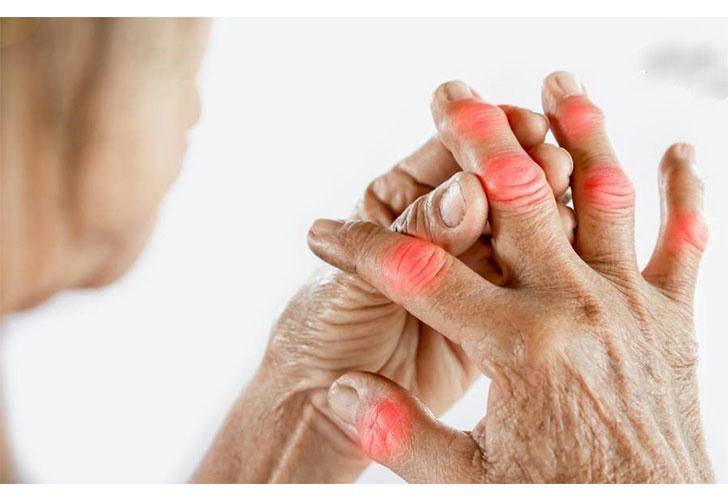
Overview of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is more prevalent in women than men and typically manifests between the ages of 35 and 50, although it can occur at any age. The condition is systemic, meaning it can affect not only the joints but also other organs such as the heart, lungs, and eyes.
Key Characteristics:
• Symmetrical Joint Involvement: RA usually affects joints on both sides of the body equally (e.g., both wrists or both knees).
• Morning Stiffness: Patients often experience stiffness in the affected joints after periods of inactivity, which can last for more than an hour.
• Joint Deformities: Over time, RA can lead to significant joint damage and deformities if not managed properly.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Symptoms can vary widely among individuals but often include:
• Pain and swelling in joints (especially in the hands, wrists, and feet)
• Morning stiffness lasting more than an hour
• Fatigue and general malaise
• Low-grade fever
• Weight loss
• Presence of rheumatoid nodules (firm lumps under the skin)
Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis remains unclear. However, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors. The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissues, leading to inflammation and damage.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing RA typically involves:
• Clinical Evaluation: A healthcare provider will assess symptoms and perform a physical examination.
• Blood Tests: Tests for rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (anti-CCP), and inflammatory markers (such as ESR and CRP) help confirm the diagnosis.
• Imaging Studies: X-rays or MRI scans may be used to assess joint damage.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, various treatment options are available to manage symptoms and slow disease progression:
1. Medications:
• Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Help reduce pain and inflammation (e.g., ibuprofen).
• Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Slow disease progression (e.g., methotrexate).
• Biologics: Target specific parts of the immune system (e.g., adalimumab).
2. Physical Therapy:
• Engaging in physical therapy can help improve joint function and mobility through tailored exercise programs.
3. Lifestyle Modifications:
• Maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, and avoiding smoking can help manage symptoms.
4. Surgery:
• In severe cases where joint damage occurs, surgical interventions such as joint replacement may be necessary.
Prevention Strategies
While RA cannot be prevented outright, certain lifestyle choices may help reduce the risk or severity:
• Healthy Diet: Consuming anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, fish high in omega-3 fatty acids, nuts, and whole grains.
• Regular Exercise: Engaging in low-impact activities such as swimming or cycling to maintain joint flexibility.
• Stress Management: Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as yoga or meditation.
Recommended Products for Pain Relief
Here are some products that can help alleviate pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis:
1. Heat Therapy Products:
• Thermophore Heating Pad: Provides moist heat therapy to soothe stiff joints and muscles.
2. Cold Therapy Products:
• Reusable Gel Ice Packs: Help reduce inflammation and numb painful areas after activity.
3. Supportive Devices:
• Wrist Braces or Splints: Provide support to inflamed joints during daily activities.
• Knee Supports: Help stabilize the knee joint during movement.
4. Topical Pain Relievers:
• Capsaicin Creams (e.g., Capzasin): Derived from chili peppers; they provide temporary relief by reducing substance P levels in the skin.
5. Supplements:
• Omega-3 Fatty Acids (Fish Oil): Known for their anti-inflammatory properties; may help reduce joint pain.
• Turmeric Curcumin Supplements: Contains curcumin which has anti-inflammatory effects that may benefit RA patients.
6. Exercise Equipment:
• Resistance Bands: Useful for gentle strength training without putting excessive strain on joints.
• Yoga Mat: Provides comfort during stretching and yoga exercises aimed at improving flexibility.
Conclusion
Rheumatoid arthritis is a complex autoimmune disease that requires comprehensive management strategies to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Understanding its symptoms, causes, treatment options, and preventive measures can empower individuals affected by RA to take control of their health. Additionally, utilizing supportive products can significantly enhance comfort during daily activities. If you suspect you have RA or are experiencing persistent joint pain, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
