AI-Powered Virtual Reality in Medical Training and Education
The medical field is changing rapidly, thanks to new technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and virtual reality (VR). These advanced tools are transforming how healthcare professionals learn, offering a more hands-on, customized, and efficient way to build critical skills and knowledge. By combining AI and VR in medical education, we are not only improving how students engage with their lessons but also enhancing patient care, making this a key development for the future of healthcare.
How AI is Changing Medical Training
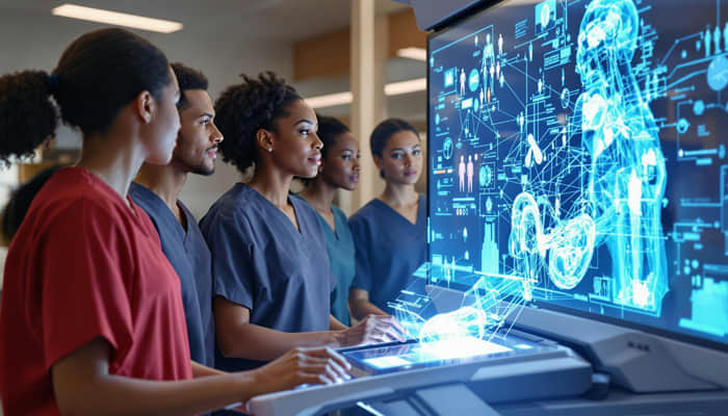

AI has long been known for handling tasks that usually need human thinking, such as decision-making and problem-solving. In medical training, AI does more than just analyze data; it creates learning environments that adapt to the specific needs of each student. Recent studies show that AI is reshaping medical education by quickly and accurately analyzing large amounts of data, providing personalized learning experiences that weren't possible before.
AI-driven personalized learning adjusts lessons to fit each student's progress and performance. Machine learning algorithms identify areas where students are strong or need improvement, offering tailored lessons and resources to help them better understand complex topics. This personalized approach makes training more effective, ensuring that students master key concepts before moving on to more advanced material.
Improving Skill Training with AI Simulations

AI plays a crucial role in creating simulations that mimic real medical situations. These simulations provide students with practical experience without any risk to actual patients. For example, AI-powered platforms let medical students interact with virtual patients who show different symptoms, helping them build essential diagnostic and decision-making skills. The instant feedback these systems provide helps students learn more effectively and boosts their confidence in their abilities.
AI also enhances decision-making in medical education by offering insights from large medical databases. This helps students and healthcare professionals make better-informed decisions, predict outcomes, and even customize treatments for individual patients. Practicing decision-making in a virtual, risk-free environment prepares students to be better healthcare providers and improves patient safety.
The Role of Virtual Reality in Medical Education
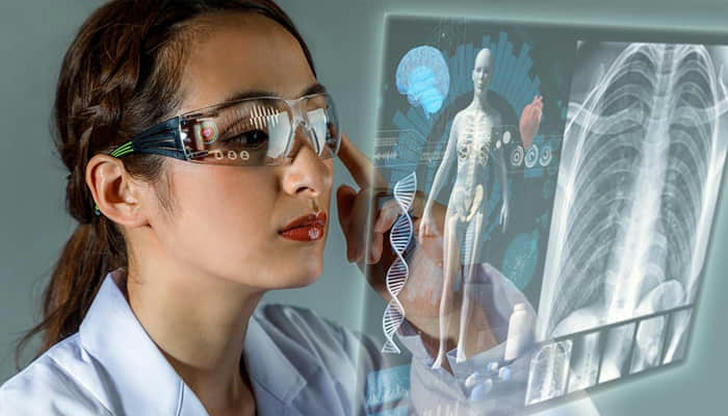

Virtual reality (VR) is another game-changing technology in medical training. VR creates immersive, interactive simulations that give students hands-on experience in a virtual world. Leading institutions like Mayo Clinic and Stanford Medicine use VR in their training programs, offering realistic simulations of clinical environments. Students can practice everything from routine exams to complex surgeries, all while getting immediate feedback.
Surgical Training and Simulation-Based Learning
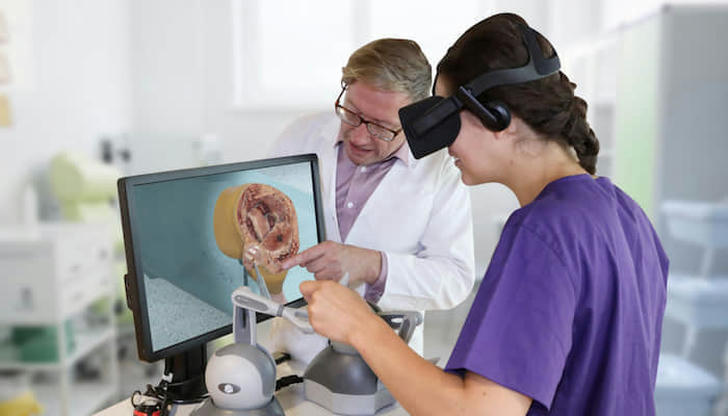
One of VR's most important uses in medical training is in surgical education. Platforms like Osso VR and FundamentalVR have developed detailed surgical simulations that let trainees practice difficult procedures over and over until they perfect them. These simulations use haptic feedback technology to simulate the physical sensations of surgery, creating a lifelike and engaging experience.
Studies show that surgeons trained with VR perform better in real surgeries compared to those who only use traditional training methods. The chance to make mistakes in a safe, virtual setting—and learn from them without consequences—helps reduce surgical errors and improve patient outcomes. This type of training is especially useful for fields like orthopedics, where surgeries like knee replacements or spinal fusions require precise skills.
Emergency Response Training with AI and VR

Beyond surgical training, AI and VR are also being used to simulate emergency medical situations. For example, the Miami Miller School of Medicine has used virtual reality to train staff on how to manage COVID-19 patients, helping them prepare for the intense challenges of a pandemic. Similarly, the University of Washington uses AI-powered simulations to train emergency response teams for high-pressure situations, such as cardiac arrests and mass casualty events.
These emergency simulations are essential for developing quick decision-making skills in a safe, controlled environment. By practicing in these virtual scenarios, healthcare professionals can improve their ability to stay calm and make the right choices when faced with real-life emergencies.
Benefits of Using AI and VR in Medical Training

Using AI and VR in medical education brings numerous advantages that traditional training methods simply can't match. These technologies make learning more interactive, engaging, and tailored to individual needs.
• Increased Engagement: Immersive technologies like VR grab students' attention by placing them in realistic scenarios where they can actively take part in the learning process. This hands-on approach helps students retain knowledge and skills more effectively.
• Personalized Learning: AI customizes educational content to suit each student's needs, allowing them to learn at their own pace. It identifies knowledge gaps and strengthens areas of expertise, making the training process more efficient and effective.
• Accessibility: VR makes medical education more accessible, especially in situations where physical resources—like cadavers for dissection—are limited. VR simulations give students the chance to explore human anatomy and practice procedures without relying on traditional resources.
• Scalability: AI-powered systems can handle large groups of students without sacrificing quality. This scalability is particularly useful in the rapidly growing healthcare field, where the demand for well-trained professionals is high.
Challenges in Implementing AI and VR in Medical Education
While AI and VR bring many benefits, there are still challenges to their widespread use in medical education.
• Cost: VR equipment and AI platforms can be expensive, making it tough for smaller institutions to adopt these technologies. On top of the initial cost, the software requires regular updates to stay functional, adding to the ongoing financial burden.
• Learning Curve: Both students and educators may find it challenging to adapt to these advanced technologies. Proper training and support are crucial to ensure users can effectively use AI and VR systems.
• Ethical Concerns: Using AI in medical training raises ethical issues, especially around data privacy and the responsibility of algorithms. Ensuring AI systems are secure and transparent is key to maintaining trust in these technologies.
Despite these challenges, the advantages of using AI and VR in medical education far outweigh the drawbacks. As technology continues to improve, the costs of these systems are likely to drop, making them more accessible to a wider range of institutions.
The Future of AI and VR in Medical Training
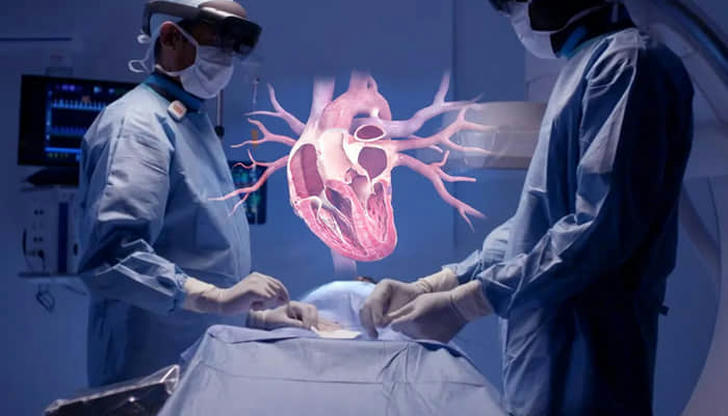
Looking ahead, AI and VR will play an even bigger role in shaping medical education. As these technologies become more advanced, they will offer even greater opportunities for personalized learning, hands-on training, and real-time feedback. Medical schools around the world are starting to see the potential of AI and VR, with many already incorporating these tools into their programs.
By embracing AI and VR, medical educators can better prepare students to handle the complexities of modern healthcare. These technologies give students the hands-on experience they need to develop the critical skills and decision-making abilities that will define the next generation of healthcare professionals.
Conclusion
AI and VR are transforming medical training by offering innovative ways to enhance learning and improve patient care. With personalized learning, realistic simulations, and immersive experiences, these technologies give students the tools they need to succeed in an increasingly complex medical field. While challenges remain in terms of cost and adaptation, the future of medical education will undoubtedly be shaped by the continued integration of AI and VR, ensuring that healthcare professionals are ready for the challenges of tomorrow's healthcare industry.
